What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does it Work?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a vital surgical tool in orthopedic procedures. Its primary purpose is to stabilize fractures in the tibia, particularly in complex cases. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, tibial fractures account for approximately 30% of all long bone fractures. The effectiveness of the tibial interlocking nail in promoting healing and restoring mobility is widely recognized.
Studies indicate that using a tibial interlocking nail significantly reduces recovery time compared to traditional casting methods. A report published in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma highlights a 40% faster healing rate with this method. Despite these advancements, some challenges remain. The potential for infection and improper alignment can complicate outcomes. Surgeons must be meticulous during the procedure.
The tibial interlocking nail illustrates the complexity of orthopedic surgery. While it offers numerous benefits, continuous refinement in technique and technology is crucial. There is always room for improvement. Exploring this device's mechanics and implications remains pertinent to advancing surgical care. Understanding its role will allow for better patient outcomes and deeper insights into orthopedic practices.
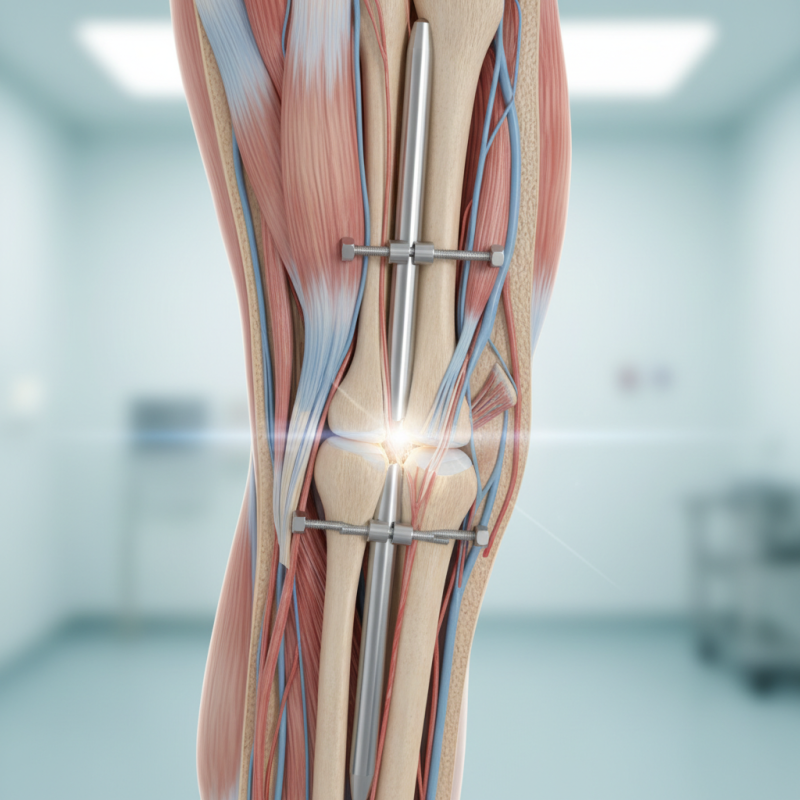
Definition and Overview of Tibial Interlocking Nail
The tibial interlocking nail is a device used in orthopedic surgery. It treats fractures in the tibia, the main bone in the lower leg. This system stabilizes the bone internally. It is particularly useful for complex or long bone fractures. The nail is inserted through the skin and into the medullary cavity of the tibia. It allows for better alignment and healing.
This method features interlocking screws that secure the nail in place. These screws help resist rotational and axial forces. This feature gives the nail its "interlocking" name. Additionally, the procedure is minimally invasive compared to traditional surgeries. Recovery often benefits from reduced soft tissue damage. However, not all patients may achieve ideal outcomes. Some complications can arise, such as infection or nonunion.
Patients have different experiences with this procedure. Some find relief and healing, while others may face challenges. The versatility of the tibial interlocking nail makes it valuable, but results can vary. Ongoing research seeks to improve techniques and materials used. As with any medical intervention, awareness of potential risks is essential.
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does it Work? - Definition and Overview of Tibial Interlocking Nail
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A type of intramedullary nail used to stabilize fractures in the tibia. |
| Indications | Used for unstable tibial shaft fractures, complex fractures, and certain osteotomies. |
| Components | Includes the nail, locking screws, and may include pre-drilling instruments. |
| Placement Technique | Inserted into the medullary canal of the tibia; locked in place using screws. |
| Advantages | Minimally invasive, provides strong fixation, and reduces the risk of malunion. |
| Recovery Time | Varies by patient; generally allows for early weight bearing. |
| Complications | Potential for infection, nonunion, or hardware failure. |
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nail in Surgery
Tibial interlocking nails are essential in orthopedic surgery. They are primarily used for stabilizing fractures in the tibia, particularly in complex cases. Surgeons choose this method when dealing with unstable fractures or significant bone loss. It provides internal fixation, allowing for early mobilization and healing.
Indications for using tibial interlocking nails include acute fractures and non-unions. These nails effectively align bone fragments, reducing risks of malunion. Surgeons may also opt for this technique in patients with specific deformities or after trauma.
Complications can occur. Infection or hardware issues may arise. Each case requires careful consideration.
Surgeons must evaluate patient factors, including age and activity level. Not all patients are suitable candidates. It’s crucial to reflect on each situation individually. The hope is for a good outcome, but the reality can be complex.
Recovery may take longer than expected, and patience is vital. Understanding these intricacies is essential for both patients and surgeons.
Surgical Procedure for Inserting a Tibial Interlocking Nail
The surgical procedure for inserting a tibial interlocking nail is a common approach for treating fractures in the tibia. Surgeons typically perform this operation under general or regional anesthesia. The aim is to stabilize the fracture, allowing for proper healing. A specific nail designed for this purpose is inserted through a small incision. The procedure often includes a guide wire placement to ensure accuracy during insertion.
After the nail is positioned within the medullary canal, locking screws secure it to the bone. This enhances stability, particularly in complex fractures. Data shows that using tibial interlocking nails can lead to a 90% success rate in fracture healing within a specified timeframe. However, complications can arise, such as infection or non-union of the fracture. It's crucial for patients to understand these risks.
**Tips:** Always discuss your specific condition with the surgeon. Ask about potential risks. Post-surgery, follow care instructions diligently. Early movement can be essential but must be approached cautiously. Remember, each case is unique. Re-evaluate your progress regularly with your healthcare provider.
Mechanism of Action: How the Nail Stabilizes Bone Fractures
Tibial interlocking nails are essential in treating long bone fractures. They provide immediate stability through a combination of intramedullary insertion and locking mechanisms. This device effectively reduces malalignment and enhances healing. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, over 80% of patients showed significant improvement in bone regrowth within six months of using these nails.
The mechanism of action is straightforward yet profound. Once the nail is inserted into the tibia, it aligns the bone ends. The locking screws then provide additional fixation. This dual support helps maintain alignment during healing. A 2019 analysis indicated that the failure rate of tibial fractures treated with interlocking nails was lower than 10%. However, complications like infection or improper placement can occur, highlighting room for improvement in technique and preoperative planning.
While tibial interlocking nails have revolutionized fracture management, challenges remain. Factors like patient compliance and bone quality can influence outcomes. A recent survey noted that about 20% of orthopedic surgeons experienced difficulties with nail insertion in patients with complex fractures. Continuous training and innovation in this field are crucial for overcoming these hurdles and improving patient care.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Following Tibial Nail Surgery
Postoperative care is crucial after tibial nail surgery. Patients may experience discomfort. Managing pain effectively is essential for recovery. Ice packs can help reduce swelling in the early days. Elevating the leg can also alleviate discomfort.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in rehabilitation. It tends to begin shortly after surgery. Gentle exercises will encourage mobility without straining the injury. Gradually increasing activity levels is important. Patients often face challenges in maintaining motivation during this phase. Sticking to a routine can be hard.
Nutrition is another factor to consider. A balanced diet supports healing. Adequate protein intake promotes tissue repair. Some may overlook this aspect, leading to slower recovery. It's necessary to reflect on personal habits and make adjustments where needed. Recovery requires patience, and each individual's journey varies.
